Benefits for Quebec
What is CETA?
- The Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) is a free trade agreement between Canada and the European Union, covering virtually all sectors and aspects of Canada-EU trade.
- Prior to CETA’s provisional application, only 25 percent of EU tariff lines on Canadian goods were duty-free.
- Following CETA’s provisional application, the EU removed tariffs on 98 percent of its tariff lines.
- After seven years, the EU will have eliminated tariffs on 99 percent of its tariff lines.
- For service providers, CETA grants the best market access that the EU has ever provided in a free trade agreement.
- CETA helps create middle-class jobs, strengthen economic relations with the EU, and boost Canada’s trade with the world’s second-largest market with over 500 million consumers and a $22 trillion GDP.
Benefits for Quebec:
- Under CETA, 98 percent of EU tariff lines are immediately duty free for Quebec goods, including information and communications technology (ICT) products, iron and steel, chemicals and plastics, machinery and equipment, and most agriculture and agri-food.
- Improved access to the EU for Quebec service suppliers in areas such as ICT services, engineering services, and other professional services.
- Enhanced labour mobility for business-related travel.
- Ability to bid on procurement contracts at all levels of EU government.
- Greater certainty, transparency, and protection for investments.
To learn more about CETA, visit our website: www.international.gc.ca/CETA
The Canadian Trade Commissioner Service provides expert advice and key contacts for exporters, partners and investors.
Contact a Trade Commissioner today: tradecommissioner.gc.ca
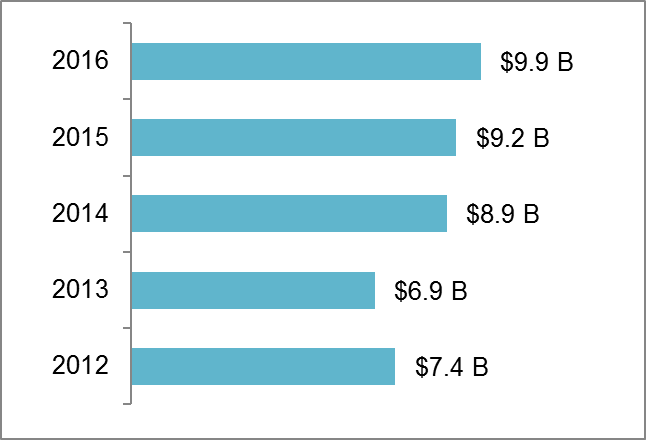
Source: Statistics Canada
Text version
- 2016: $9.9 B
- 2015: $9.2 B
- 2014: $8.9 B
- 2013: $6.9 B
- 2012: $7.4 B
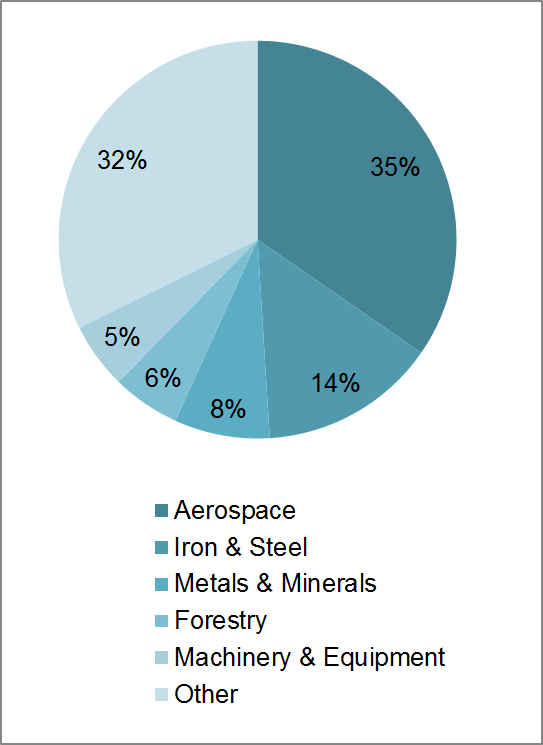
Source: Statistics Canada
Text version
- Aerospace: 35%
- Iron & Steel: 14%
- Metals & Minerals: 8%
- Forestry: 6%
- Machineray & Equipment: 5%
- Other: 32%
Information and Communications Technology (ICT) Services
- The EU, as the world’s largest importer of telecommunications, computer, and information services, holds significant potential for Quebec’s ICT companies.
- ICT companies that provide services related to technical testing and analysis, data processing, communication, and software implementation can compete on an equal footing as EU services suppliers and receive better treatment than most of their non-EU competitors.
- CETA facilitates the ability of professionals in the ICT and video game industry to conduct business and work temporarily in the EU, for example, to attend meetings, negotiate sales, and deliver specialized ICT solutions.
- In the area of e-commerce, CETA includes a permanent moratorium on customs duties, fees, or charges for digital products transmitted between Canada and the EU.
- Enhanced access to EU government procurement also provides opportunities for Quebec suppliers in a broad range of ICT services, including: technical testing and analysis, data processing, maintenance and repair, and software consulting, design and implementation.
- For procurement opportunities, suppliers can access tender notices for all CETA-covered procurements using the Tenders Electronic Daily portal (TED, at ted.europa.eu).
Professional Services
- The EU is the world’s largest importer of services and demand is strong in areas of strength for Quebec businesses, such as architecture and engineering, management, and technical consulting.
- Under CETA, professional services firms based in Quebec benefit from improved and more secure access to the EU market.
- CETA’s labour mobility provisions also facilitate the ability of the province’s professionals to conduct business and provide services in the EU market.
- CETA provides new access to the EU procurement market, valued at $3.3 trillion annually, in a broad range of services of interest to Quebec firms, including in areas of engineering and architecture, urban planning, technical consulting, and marketing and management.
Manufacturing
- CETA makes Quebec’s manufactured goods more competitive in the EU market.
- Under CETA, Quebec exporters enjoy duty-free, quota-free market access to the EU for a broad range of products, including:
| Pre-CETA tariffs | Under CETA | |
|---|---|---|
| iron and steel products | up to 5.7% | 0% |
| machinery and equipment | up to 8% | 0% |
| gas turbines and parts | up to 4.1% | 0% |
| ICT products | up to 14% | 0% |
| chemicals and plastics | up to 6.5% | 0% |
- Quebec manufacturers will be able to have certain goods (such as machinery and parts, construction products, electrical and electronic equipment) tested to EU standards by a certification body in Canada, and the results of the tests will be recognized by the EU, thereby avoiding testing duplication and reducing costs.
- Under CETA, Quebec companies can also supply goods and select services to all levels of EU government, including utilities and thousands of regional and local government entities.
- For procurement opportunities, suppliers can access tender notices for all CETA-covered procurements using the Tenders Electronic Daily portal (TED, at ted.europa.eu).
Agriculture
- Under CETA, 94% of EU agricultural tariff lines became duty-free for Canadian goods, boosting the competitiveness of Quebec’s agricultural and agri-food exports to the EU. Many remaining EU tariff lines will be phased out over a period of 7 years.
- CETA’s comprehensive tariff elimination plays to many of the region’s strengths, including:
| Pre-CETA tariffs | Under CETA | |
|---|---|---|
| maple syrup | up to 8% | 0% |
| frozen blueberries | up to 9.6% | 0% |
| sweet dried cranberries | 17.6% | 0% |
| sweet potatoes | 3% | 0% |
| condiments and sauces | up to 10.2% | 0% |
| dog and cat food | up to €948/tonne | 0% |
- For many processed foods, EU tariffs can be complex and trade-restrictive. CETA has eliminated all tariffs on processed foods (with the exception of sweet corn and refined sugar), providing Quebec food manufacturers with an advantage over many competitors entering the EU market.
| Pre-CETA tariffs | |
|---|---|
| processed cereals | up to €54.30/100 kg |
| breads, pastries, and cakes | start at €3.80/100 kg |
| food preparations | start at 12.8% |
| toffees, caramel candy, and chocolate | up to 9% + EA MAX 18.7% + AD S/Z |
Fish and Seafood
- The EU is the world’s largest importer of fish and seafood, accounting for 28% of global fish and seafood imports in 2016.
- CETA helps make the region’s fish and seafood exports more competitive in the EU market.
- Before CETA, EU tariffs on fish and seafood products averaged 11% and could be as high as 25%. Following CETA’s provisional application, the EU eliminated tariffs on almost 96% of its fish and seafood tariff lines, with remaining tariffs to be phased out over 3, 5, or 7 years. For products of interest to Quebec’s fish and seafood industry:
| Pre-CETA tariffs | Under CETA | |
|---|---|---|
| frozen shrimp | 12% | 0% |
| cooked and peeled shrimp in retail packages | 20% | 0% |
| live lobster | 8% | 0% |
| frozen lobster | up to 16% | tariff phase-out over 3 years |
| processed lobster | 20% | tariff phase-out over 5 years |
| Scallops | 8% | 0% |
| dried and salted cod | 13% | 0% |
Forestry
- The EU is the world’s third largest importer of forest products and presents new opportunities for the region’s producers.
- Under CETA, Quebec’s forestry exports enjoy duty-free, quota-free market access to the EU, including for products such as:
| Pre-CETA tariffs | Under CETA | |
|---|---|---|
| plywood | 7% to 10% | 0% |
| veneer sheets | up to 4% | 0% |
| oriented strand board | 7% | 0% |
| fiberboard | 7% | 0% |
- Quebec service suppliers benefit from open markets to provide technical expertise in a wide range of areas, including: wood lot management, mapping, surveying, re-forestation, timber evaluation, forest damage assessment, and logging-related services.
- CETA makes it easier for the region’s highly-skilled professionals to conduct business and provide forestry-related services in the EU.
- CETA could provide new access to the EU procurement market, valued at $3.3 trillion annually, in a broad range of forestry services of interest to Quebec, including: supply chain analysis and optimization, forest resources inventory and remote sensing, mapping and data processing, forest management and operation logistics, turn-key plant set-up and modernization, and manufacturing management and control.
- For procurement opportunities, suppliers can access tender notices for all CETA-covered procurements using the Tenders Electronic Daily portal (TED, at ted.europa.eu).
Mining, Metals and Minerals
- The EU is the world’s largest importer of metals and minerals and its consumption has grown rapidly over the past decade.
- CETA has eliminated all tariffs on the region’s exports of metals and minerals, making these products more competitive in the EU market. For example:
| Pre-CETA tariffs | Under CETA | |
|---|---|---|
| unwrought aluminum | 3% | 0% |
| unwrought aluminum alloys | 6% | 0% |
| titanium powders and alloys | up to 7% | 0% |
| copper wire | 4.8% | 0% |
| unwrought zinc | 2.5% | 0% |
- Quebec’s mining industry benefits from preferential access to provide technical and advisory services in the EU. Service providers from Quebec can compete on equal footing with EU service providers and receive better treatment than most of their non-EU competitors.
- CETA’s temporary entry provisions make it easier for professionals in the mining sector to conduct business in the EU, for example, to attend meetings, negotiate sales, and provide engineering and technical consulting services.
- CETA spurs investment by providing Canadian and EU investors in the mining industry with greater certainty, transparency, and protection for their investments.
Aerospace and Aviation
- CETA helps Canadian aerospace and aviation companies expand their presence in the EU.
- Canadian aerospace companies benefit from improved access in many EU markets compared to other non-EU competitors.
- CETA makes it easier for Quebec’s aerospace companies to provide services in the EU in areas such as engineering, aircraft maintenance and repair, technical testing and analysis, and research and development, which enhances the sector’s ability to offer its customers after-sale services abroad.
Life Sciences and Innovation
- Previous EU tariffs on medical equipment could be as high as 8%. CETA eliminated all EU tariffs on medical equipment, making Quebec’s exports more attractive in the EU market.
- CETA’s services and labour mobility provisions provide better and more secure access for companies that deliver specialized services in the EU.
- Quebec’s exporters of medical equipment gain access to EU procurement opportunities at all levels of EU government, including at the sub-central level by hospitals and universities.
- Under CETA, new intellectual property protections for innovators also make Canada a more attractive environment for EU companies investing in life sciences.
- Date modified: