Archived information
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please contact us to request a format other than those available.
Report on exports of military goods from Canada - 2015
PDF Version (310 KB)Footnote *
I. Introduction
The 2015 Report on the Export of Military Goods from Canada is a voluntary report tabled in the Parliament of Canada to increase the transparency of Canadian arms exports. This Report has been produced since 1990. The last edition covered 2014 and was tabled in Parliament alongside this report.
Data for this Report is assembled following the end of the calendar year, and verified against information received from Canadian industry.
Data covering Canadian exports of military goods is also captured in two other key reports: the Annual Report on the Administration of the Export and Import Permits Act which is tabled in Parliament (a legal requirement of the Act); and Canada’s submission to the United Nations Register of Conventional Arms (UNCAR).
Summary of Key Data
For the 2014 calendar year, Canada’s total exports permitted under the Export and Import Permits ActFootnote 1 of military goods and technology amounted to approximately $676 million.
- The major share ($503.6 million or 79.4%) went to member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) or other countries included on Canada’s Automatic Firearms Country Control List (AFCCL).
- The United Kingdom was the largest export destination outside of the United States in 2015, receiving approximately $100 million in military exports (accounting for 14.8% of the total value of military exports).
- Saudi Arabia was the second largest destination of Canadian military exports in 2015, receiving $95.6 million in military exports (accounting for 14.1% of Canadian military exports).
- Seven NATO countries were in the top twelve destinations for the same period: the United Kingdom, Germany, France, Belgium, Netherlands, Spain and Italy.
- Hong Kong and Algeria, the fourth and eighth-largest destinations for Canadian military exports respectively, were the only non-NATO and non-AFCCL countries in the top twelve. .
II. Export Controls
Canada’s export controls are rigorous and in line with those of our principal allies and partners in the major export controls regimes. A key priority of Canada’s foreign policy is the maintenance of peace and security. To this end, the Government of Canada strives to ensure that, among other policy goals, Canadian exports are not prejudicial to peace, security or stability in any region of the world or within any country.
This policy is implemented primarily through Canada’s system of export controls, as authorized by the Export and Import Permits Act (EIPA). This law requires those who wish to export from Canada any items included on the Export Control List to obtain, prior to shipment, an export permit issued by Global Affairs Canada.Footnote 2 The Export Control List includes military, dual-use, and strategic goods and technology, all United States-origin goods and technology, and a limited number of items that are controlled for economic reasons or further to Canada’s international trade agreements.
Military Goods and Technology
The military goods and technology described in this report are those included in Group 2 (“Munitions List”) of the Export Control List. Items listed in Group 2 are “specially designed or modified for military use.”
The Group 2 (Munitions List) goods and technologies include such items as ground vehicles, firearms, ammunition, imaging equipment, etc. made specifically for military use (a full list of these items is included in Table 5). Other controlled items appearing elsewhere on the Export Control List (such as dual-use and strategic items) are not featured in this report as they are not specially designed for military use.
Canada prohibits the export of arms and related materiel to countries that are under United Nations Security Council arms embargos via the United Nations Act, and also has autonomous sanctions in place against specific countries under the Special Economic Measures ActFootnote 3, which prohibit the export of specific goods and technology to those countries and/or to listed individuals and entities within those countries.
Canada also prohibits the sale of automatic firearms to countries that are not on Canada’s Automatic Firearms Country Control List as established under the authority of the EIPA. Furthermore, the EIPA also provides for an Area Control List, which is a list of countries to which the Governor-in-Council deems it necessary to control the export or transfer of any goods or technology. Export permits are normally issued only for those goods and technology that respond to humanitarian needs or circumstances. Currently, only two countries – Belarus and North Korea – are listed on the Area Control List.
Under export control policy guidelines approved in 1986 by Cabinet, Canada closely controls the export of military goods and technology to countries:
- that pose a threat to Canada and its allies;
- that are involved in or under imminent threat of hostilities;
- that are under United Nations Security Council sanctions; or
- whose governments have a persistent record of serious violations of the human rights of their citizens, unless it can be demonstrated that there is no reasonable risk that the goods might be used against the civilian population.
Additional policy goals of Canada’s overall export controls regime include:
- ensuring that exports do not contribute to the development of nuclear, biological or chemical weapons of mass destruction, or of their delivery systems; and
- ensuring that exports are consistent with existing economic sanction provisions.
Once an application to export goods or technology has been received, it is reviewed against these criteria, which may include wide-ranging consultations among geographic, human rights, international security and defence-industry experts at Global Affairs Canada (including at Canada’s overseas diplomatic missions), the Department of National Defence and, as necessary, other government departments and agencies. Through such consultations, export permit applications are assessed for their consistency with Canada’s foreign and defence policies. Regional peace and stability, including civil conflict and human rights, as well as the possibility of unauthorized transfer or diversion of the exported goods and technology, are actively considered.
A key consideration in the review of each application is the end-use and end-user of the exported article. Careful attention is paid to end-use documentation in an effort to ensure that the export is intended for a legitimate end-user and will not be diverted to ends that could threaten the security of Canada, its allies or civilians.
Military goods and technology listed in Group 2 of the Export Control List generally are exported for one of the following purposes:
- sales to military and, in some cases, police forces or other government agencies;
- sales of parts and components for the production of new goods;
- repairs of military equipment in Canada for foreign customers, and shipments of spare parts; and
- sales to private individuals (sales of, non-restricted or restricted firearms).Footnote 4
Canada’s defence industry makes a valuable contribution to the nation’s prosperity and employs tens of thousands of Canadians. It develops high-technology products and is closely integrated with counterparts in allied countries.
Canada’s export controls are based on our participation in the four major export control multilateral regimes, as explained further in section III. Canada’s export controls are not intended to hamper legitimate trade but seek to balance the economic and commercial interests of Canadian business with the national interest of Canada. Canada’s defence industry provides the Canadian Forces, as well as the armed forces of our allies and partners, with the equipment, munitions and spare parts necessary to meet operational needs.
Notes on the Export of Firearms
Most firearms exports from Canada are intended for sporting or other recreational use and are not for military use. Steps are taken to ensure that items are not diverted into the illegal arms trade or used to fuel local violence. Canadian diplomatic missions and other sources may provide information about destination countries’ firearms control laws, procedures and enforcement practices, and are often called upon to validate import permits and licenses, end-user assurances, and consignee information. Where concerns exist about a proposed export, the application may be referred to the Minister of Foreign Affairs for decision.
Certain prohibited firearms, weapons, devices, or components thereof that are included on the Export Control List may be exported only to countries listed on the Automatic Firearms Country Control List and then only to consignees that are government entities or are authorized by government entities.Footnote 5
In order for a country to be added to the Automatic Firearms Country Control List, Canada must have concluded an inter-governmental defence, research, development and production arrangement with that country. In 2014, three new countries were added to the Automatic Firearms Country Control List: Chile, Peru and the Republic of Korea (South Korea). The full list of countries on the Automatic Firearms Country Control List may be found in Table 6.
III. International Cooperation on Military Trade
Multilateral action is an important means of promoting international peace and security. Canada supports and participates in a range of arms control and non-proliferation activities, working closely with like-minded countries.Footnote 6
Wassenaar Arrangement
Most items have been included on the Export Control List because of Canada’s commitments to like-minded countries that participate in multilateral export control regimes or because of Canada’s obligations as a signatory to international agreements that seek to control and monitor the movement of sensitive goods and technology.
The control regime that deals with the military goods and technology covered in Group 2 of the Export Control List is the Wassenaar Arrangement on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies,Footnote 7 founded in 1996. The “Initial Elements” define the objectives of the Arrangement as, inter alia:
“to contribute to regional and international security and stability, by promoting transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies, thus preventing destabilising accumulations.”
Through national policies, the 41 Participating States seek to ensure that transfers of items covered by the common control lists do not contribute to the development or enhancement of military capabilities that have the potential to undermine regional and global security and stability. Participating States also commit to take every precaution to ensure that such goods and technologies are not diverted to illegitimate end-uses.
United Nations Register of Conventional Arms
Canada continues to actively promote greater transparency in the trade of conventional arms. In 1991, Canada was a founding contributor to the United Nations Register of Conventional Arms (UNCAR), to which governments voluntarily supply data on unit number of imports and exports of seven major categories of conventional weapon systems.Footnote 8 The annually updated Register makes a significant contribution to transparency, confidence-building and enhanced global security. Each year since the inception of the Register, more than 90 governments on average have made submissions to it; of these, about 70 have done so consistently, including Canada. As a result, the Register has become an important and authoritative source of information.
Canada is also one of a growing number of countries that voluntarily submit data to the Register on military holdings and on procurement through national production. This information goes beyond the minimum currently required by the United Nations. Canada’s submission to UNCAR is available on the Internet.
Trade in Small Arms and Light Weapons
Canada, in cooperation with like-minded partners, is looking at ways to address the problem of illicit small-arms proliferation, which can undermine security and development efforts and contribute to human suffering. Canada has adopted an integrated approach, addressing the arms-control, crime-prevention and peace-building dimensions of the issue at all levels. Such an approach targets supply and transit issues, and seeks to cope with post-conflict surplus stocks and reduce the demand for weapons.
Canada promotes measures designed to achieve transparency in legal transfers of small arms and light weapons. Aspects under review include codes of conduct and transparency initiatives. Canada’s own procedures are strict and seek to ensure a high level of control over exports of small arms.
IV. Military Export Statistics
The statistics contained in this Report are obtained from utilization reports which must be provided to Global Affairs Canada as a condition of using export permits for military goods and technology. These reports include the country of destination, a description of the goods exported, their quantity and their value in Canadian dollars.
Please note that further details related to export transactions (for example, names of exporting companies, financial values of individual contracts and transactions, and details of the specific technologies being exported) are protected due to the commercially confidential nature of such information.
Export controls apply to all foreign destinations. However, due to close and long-standing military cooperation with the United States, including the integrated nature of North America’s defence industry, permit exemptions apply to most Group 2 exports destined for final use in that country. Statistics related to exports of military goods and technology to the United States therefore are not reported here.
Data on Canadian military exports may be available from other sources such as Statistics Canada. It should be noted that these figures are derived from data collected by the Canada Border Services Agency based on the Harmonized Commodity Description Coding System (HS), and may include non-military goods such as commercial computers, civil-certified aircraft, guns and ammunition designed exclusively for industrial uses, such as the lighting of gas flares at oil wells, or other civilian equipment. Since there is no direct correlation between the commodity codes used by Statistics Canada and the Export Control List numbers, and because each source uses different methods of data collection, a meaningful comparison of the information from these sources is extremely difficult.
An internationally accepted standard for statistics on worldwide military trade is UNCAR (described above). However, the Register limits itself to the number of exported units of complete weapon systems and does not include parts, components or the wide assortment of non-lethal support systems (such as radar equipment, simulators and software designed for military use, etc.) that make up the majority of Canada’s military exports.
Global Affairs Canada also produces an Annual Report to Parliament on the “Administration of the Export and Import Permits Act,” which is a statutory requirement in the Act. This Report provides an overview of permit data (including for Group 2 items) and service standards, which also includes Group 2 (Munitions List) permits. Following tabling in Parliament, this Report is also available on the Global Affairs Canada website.
Data interpretation notes
The following data interpretation notes apply to Tables 3, 4, 6 and 7:
i) Procurement contracts awarded by governments may have very high values and extended delivery schedules; a single contract may account for a large share of total military exports in a given year. Major changes in totals from one year to another may be explained by the beginning or end of a small number of large contracts.
ii) The tables do not report exports of military goods to the United States, which are roughly estimated to account for over half of Canada’s exports of military goods and technology each year.
iii) The Export Control List (ECL) item numbers used in Tables 6 and 7 are explained with illustrative examples in Table 5. The full ECL, which consists of detailed descriptions of all goods and technology controlled under the Export and Import Permits Act, can be found in “A Guide to Canada’s Export Controls”, which is available on the Internet at www.exportcontrols.gc.ca.
iv) Table 4 reports annual values of total exports of military goods and technology by destination country. Table 6 breaks down the value of exports to individual countries according to the ECL item number. However, the sum total of exports by ECL item number to an individual country calculated from Table 6 may not equal the total value of exports to that destination reported in Table 4: since goods or technology included in a single export permit may be classified under multiple ECL item numbers, Tables 6 and 7 contain some double-counting.
v) Table 7 indicates a number of very low-value exports of “technology” controlled under item 2-22 of the ECL. Exports of this nature often cannot easily be quantified. For this reason, “lots” rather than unit quantities are commonly used where exports of technology may be transferred via different intangible means. For zero-value technology transactions, a nominal value (e.g., $1 to $50) is assigned. The inclusion of such data within the Military Report is consistent with past practice.| Exports | Value | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total exports of military goods and technologyFootnote 9 | $ 676,431,004 | 100% | |
| Exports to destinations categorized by Human Development Index (HDI) levelFootnote 10 | |||
| Very High HDI countries | $ 562,328,882 | 83.1% | |
| High HDI countries | $ 82,400,846 | 12.2% | |
| Medium HDI countries | $ 26,660,609 | 3.9% | |
| Low HDI countries | $ 4,575,647 | 0.7% | |
| Not HDI ranked | $ 465,019 | 0.1% | |
| Exports to destinations categorized by defence Relationship | |||
| NATOFootnote 11 | $ 299,935,144 | 59.3% | |
| Non-NATO AFCCLFootnote 12 | $ 203,652,690 | 20.1% | |
| Other | $ 172,843,170 | 20.6% | |
| Group | Issued | Returned Without Action | Withdrawn | Denied |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (Dual-Use List) | 2,202 | 86 | 41 | 2 |
| Group 2 (Munitions List) | 3,391 | 168 | 80 | 4 |
| Group 3 (Nuclear Non-Proliferation List) | 128 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
| Group 4 (Nuclear-Related Dual-Use List) | 113 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| Group 5 (Miscellaneous Goods and Technology) | 187 | 11 | 40 | 2 |
| Group 6 (Missile Technology Control Regime List) | 98 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Group 7 (Chemical and Biological Weapons Non-Proliferation List) | 43 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| Others | 125 | 100 | 218 | 0 |
| Totals | 6,287 | 383 | 384 | 8 |
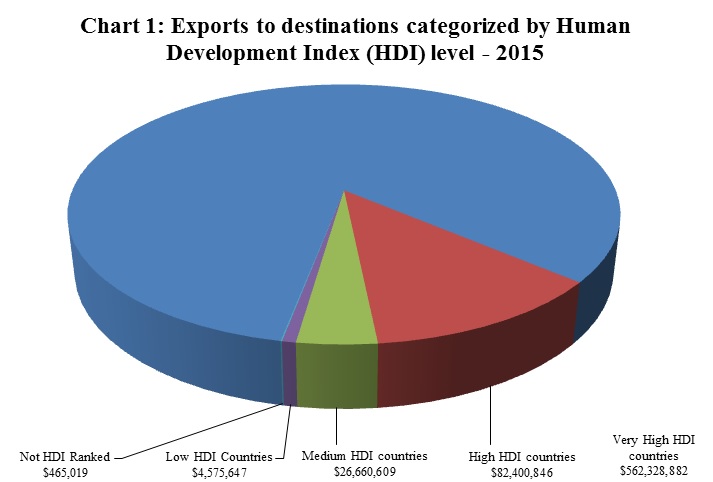 Footnote 14
Footnote 14Chart 1 Text Alternative
| 2015 | |
|---|---|
| Not Ranked | $465,019 |
| Low HDI Countries | $4,575,647 |
| Medium HDI Countries | $26,660,609 |
| High HDI Countries | $82,400,846 |
| Very High HDI Countries | $562,328,882 |
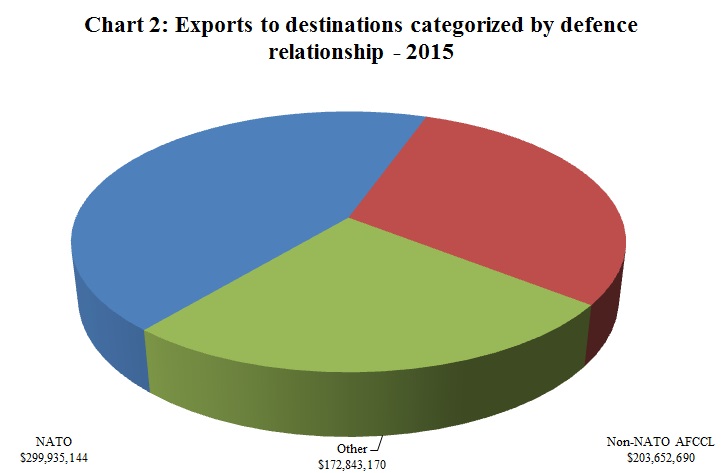 Footnote 15
Footnote 15Chart 2 Text Alternative
| 2015 | |
| NATO | $299,935,144 |
| Non-NATO AFCCL | $203,652,690 |
| Other Destinations | $172,843,170 |
| Export Destination | Value Exported |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | $100,092,212 |
| Saudi Arabia | $95,640,705 |
| Hong Kong | $48,041,540 |
| Australia | $45,904,639 |
| Germany | $45,868,372 |
| France | $30,153,761 |
| Algeria | $28,590,158 |
| Belgium | $26,663,805 |
| Netherlands | $22,070,879 |
| Spain | $19,879,107 |
| Peru | $19,585,265 |
| Italy | $15,337,638 |
| Export Destination | Value Exported ($) |
|---|---|
| Algeria | $28,590,158 |
| Argentina | $52,922 |
| Armenia | $16,364 |
| Australia | $45,904,639 |
| Austria | $520,428 |
| Azerbaijan | $41,128 |
| Bahrain | $98,603 |
| Bangladesh | $241 |
| Belgium | $26,663,805 |
| Belize | $42,871 |
| Botswana | $568,832 |
| Brazil | $2,195,491 |
| Brunei Darussalam | $450,082 |
| Bulgaria | $700 |
| Chile | $54,285 |
| China | $41,585 |
| Colombia | $522,203 |
| Congo | $7,904 |
| Croatia | $10,714 |
| Cyprus | $119,000 |
| Czech Republic | $426,994 |
| Denmark | $8,810,442 |
| Ecuador | $520,343 |
| Egypt | $13,589,334 |
| Estonia | $70,600 |
| Finland | $521,770 |
| France | $30,153,761 |
| Georgia | $508 |
| Germany | $45,868,372 |
| Greece | $132,114 |
| Greenland | $39,878 |
| Guatemala | $6,000 |
| Guyana | $58,000 |
| Hong Kong | $48,041,540 |
| Hungary | $5,107 |
| India | $5,430,876 |
| Indonesia | $742,370 |
| Iraq | $1,925,769 |
| Ireland | $528,793 |
| Israel | $7,838,849 |
| Italy | $15,337,638 |
| Japan | $13,805,051 |
| Jordan | $5,350,624 |
| Kazakhstan | $127,984 |
| Kenya | $2,839,593 |
| Latvia | $2,114 |
| Lebanon | $762 |
| Liechtenstein | $636 |
| Lithuania | $12,753 |
| Luxembourg | $12,021,454 |
| Madagascar | $799 |
| Malaysia | $886,077 |
| Malta | $222 |
| Mexico | $2,124,475 |
| Montenegro | $153,932 |
| Morocco | $46,608 |
| Namibia | $930 |
| Netherlands | $22,070,879 |
| New Zealand | $5,726,311 |
| Nigeria | $1,702,796 |
| Norway | $7,991,706 |
| Oman | $2,554,784 |
| Peru | $19,585,265 |
| Philippines | $192,490 |
| Poland | $2,116,541 |
| Portugal | $660,909 |
| Puerto Rico | $35,154 |
| Qatar | $660,000 |
| Romania | $1,991 |
| Russian Federation | $1,599 |
| Saudi Arabia | $95,640,705 |
| Singapore | $11,731,436 |
| Slovakia | $26,271 |
| Slovenia | $22,224 |
| South Africa | $4,084,773 |
| South Korea | $14,248,236 |
| Spain | $19,879,107 |
| St. Kitts-Nevis | $450 |
| Sweden | $13,041,594 |
| Switzerland | $7,144,524 |
| Taiwan | $429,415 |
| Tanzania | $460 |
| Thailand | $6,094,897 |
| Tunisia | $5,989,166 |
| Turkey | $7,556,736 |
| Ukraine | $155,135 |
| United Arab Emirates | $3,629,728 |
| United Kingdom | $100,092,212 |
| Vietnam | $6,482 |
| Yemen | $32,000 |
| Grand Total | $676,431,004 |
| Export Control List Item | Illustrative ExamplesFootnote 18 |
|---|---|
| 2-1 | Smooth-bore weapons with a calibre of less than 20 mm, other arms and automatic weapons with a calibre of 12.7 mm or less and accessories |
| 2-2 | Smooth-bore weapons with a calibre of 20 mm or more, other weapons or armament with a calibre greater than 12.7 mm, projectors and accessories |
| 2-3 | Ammunition and fuse-setting devices, and specially designed components |
| 2-4 | Bombs, torpedoes, rockets, missiles, other explosive devices and charges, and related equipment and accessories specially designed for military use; and specially designed components |
| 2-5 | Fire control, related alerting and warning equipment, and related systems; test and alignment and countermeasure equipment specially designed for military use; and specially designed components and accessories |
| 2-6 | Ground vehicles and components |
| 2-7 | Chemical or biological toxic agents, riot control agents, radioactive materials, and related equipment, components and materials |
| 2-8 | Energetic materials and related substances |
| 2-9 | Vessels of war, special naval equipment and accessories, and components specially designed for military use |
| 2-10 | Aircraft, lighter-than-air vehicles, unmanned airborne vehicles, aero-engines and aircraft equipment, related equipment and components, specially designed or modified for military use |
| 2-11 | Electronic equipment, military spacecraft and components not controlled elsewhere |
| 2-12 | High-velocity kinetic energy weapon systems and related equipment, and specially designed components |
| 2-13 | Armoured or protective equipment and constructions and components |
| 2-14 | Specialized equipment for military training or for simulating military scenarios, simulators specially designed for training in the use of any firearm or weapon controlled in 2-1 or 2-2, and specially designed components and accessories |
| 2-15 | Imaging or countermeasure equipment, specially designed for military use, and specially designed components and accessories |
| 2-16 | Forgings, castings and other unfinished products the use of which in a controlled product is identifiable by material composition, geometry or function, and which are specially designed for any products controlled in 2-1 to 2-4, 2-6, 2-9, 2-10, 2-12 or 2-19 |
| 2-17 | Miscellaneous equipment, materials, libraries and specially designed components |
| 2-18 | Equipment for the production of products referred to in the Munitions List |
| 2-19 | Directed energy weapon systems, related or countermeasure equipment and test models, and specially designed components |
| 2-20 | Cryogenic and superconductive equipment, and specially designed components and accessories |
| 2-21 | Software |
| 2-22 | Technology |
Export Control List # | Value Exported ($) |
|---|---|
| 2-1 | $34,539,768 |
| 2-2 | $3,938,393 |
| 2-3 | $27,257,067 |
| 2-4 | $7,222,684 |
| 2-5 | $21,159,887 |
| 2-6 | $128,062,666 |
| 2-7 | $692,580 |
| 2-9 | $36,957,218 |
| 2-8 | $2,947,072 |
| 2-10 | $150,829,343 |
| 2-11 | $34,445,697 |
| 2-12 | - |
| 2-13 | $2,548,050 |
| 2-14 | $24,601,746 |
| 2-15 | $112,820,013 |
| 2-16 | $3,226,625 |
| 2-17 | $6,446,995 |
| 2-18 | $7,741,064 |
| 2-19 | - |
| 2-20 | - |
| 2-21 | $51,446,297 |
| 2-22 | $29,157,251 |
| Export Destination | Export Control List # | Value Exported ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Algeria | 2-10 | $53,149 |
| 2-14 | $353,422 | |
| 2-15 | $25,452,647 | |
| 2-18 | $2,685,377 | |
| 2-22 | $45,563 | |
| Argentina | 2-1 | $30,190 |
| 2-3 | $105 | |
| 2-10 | $22,527 | |
| 2-22 | $100 | |
| Armenia | 2-1 | $16,364 |
| Australia | 2-1 | $342,471 |
| 2-2 | $357,919 | |
| 2-4 | $15,351 | |
| 2-5 | $2,237,221 | |
| 2-6 | $1,435,939 | |
| 2-7 | $8,620 | |
| 2-9 | $1,814,784 | |
| 2-10 | $20,148,912 | |
| 2-11 | $1,138,449 | |
| 2-13 | $884,957 | |
| 2-14 | $5,429,479 | |
| 2-15 | $3,680,064 | |
| 2-16 | $17,394 | |
| 2-18 | $226,644 | |
| 2-21 | $6,329,741 | |
| 2-22 | $2,090,761 | |
| Austria | 2-1 | $152,161 |
| 2-3 | $4,100 | |
| 2-5 | $27,576 | |
| 2-6 | $124,525 | |
| 2-15 | $114,615 | |
| 2-21 | $97,180 | |
| 2-22 | $270 | |
| Azerbaijan | 2-5 | $41,128 |
| Bahrain | 2-6 | $74,852 |
| 2-15 | $15,567 | |
| 2-18 | $8,184 | |
| Bangladesh | 2-1 | $241 |
| Belgium | 2-1 | $11,150,144 |
| 2-3 | $3,674,101 | |
| 2-5 | $2,702,876 | |
| 2-6 | $4,441,661 | |
| 2-8 | $1,529,850 | |
| 2-10 | $867,686 | |
| 2-11 | $58,330 | |
| 2-15 | $1,204,669 | |
| 2-16 | $28,984 | |
| 2-17 | $1,892,974 | |
| 2-21 | $1,538,233 | |
| 2-22 | $40,075 | |
| Belize | 2-1 | $26,967 |
| 2-3 | $15,904 | |
| Botswana | 2-7 | $232 |
| 2-10 | $568,600 | |
| Brazil | 2-1 | $861,327 |
| 2-3 | $16,050 | |
| 2-6 | $768,547 | |
| 2-7 | $33,553 | |
| 2-10 | $111,365 | |
| 2-11 | $361,847 | |
| 2-14 | $8,402 | |
| 2-17 | $34,400 | |
| Brunei Darussalam | 2-14 | $213,771 |
| 2-21 | $10,200 | |
| 2-22 | $226,111 | |
| Bulgaria | 2-1 | $700 |
| Chile | 2-1 | $4,206 |
| 2-10 | $15,448 | |
| 2-15 | $1,559 | |
| 2-18 | $252 | |
| 2-21 | $22,720 | |
| 2-22 | $10,100 | |
| China | 2-5 | $30,465 |
| 2-11 | $11,120 | |
| Colombia | 2-5 | $4,791 |
| 2-6 | $8,790 | |
| 2-10 | $508,622 | |
| Congo | 2-11 | $7,904 |
| Croatia | 2-1 | $10,714 |
| Cyprus | 2-1 | $119,000 |
| Czech Republic | 2-1 | $75,420 |
| 2-3 | $4,140 | |
| 2-4 | $9,108 | |
| 2-11 | $33,869 | |
| 2-13 | $304,458 | |
| Denmark | 2-1 | $2,962,401 |
| 2-6 | $1,010,052 | |
| 2-10 | $2,503,580 | |
| 2-11 | $474,512 | |
| 2-15 | $1,759,891 | |
| 2-18 | $93,272 | |
| 2-22 | $2,406,026 | |
| Ecuador | 2-6 | $430,000 |
| 2-15 | $90,343 | |
| Egypt | 2-11 | $12,600 |
| 2-15 | $13,576,734 | |
| Estonia | 2-1 | $4,485 |
| 2-11 | $26,115 | |
| 2-22 | $40,000 | |
| Finland | 2-1 | $17,878 |
| 2-6 | $32,316 | |
| 2-10 | $272,302 | |
| 2-11 | $92,698 | |
| 2-15 | $102,500 | |
| 2-22 | $4,077 | |
| France | 2-1 | $813,261 |
| 2-2 | $2,400 | |
| 2-3 | $813,948 | |
| 2-4 | $516,550 | |
| 2-5 | $86,313 | |
| 2-6 | $1,475,807 | |
| 2-9 | $619,272 | |
| 2-10 | $10,885,108 | |
| 2-11 | $1,293,383 | |
| 2-13 | $168,596 | |
| 2-14 | $62,100 | |
| 2-15 | $11,097,378 | |
| 2-17 | $228,437 | |
| 2-18 | $414,498 | |
| 2-21 | $1,161,693 | |
| 2-22 | $658,325 | |
| Georgia | 2-1 | $508 |
| Germany | 2-1 | $147,193 |
| 2-2 | $220,000 | |
| 2-3 | $56,010 | |
| 2-4 | $289,935 | |
| 2-5 | $3,578,068 | |
| 2-6 | $2,262,335 | |
| 2-9 | $201,204 | |
| 2-8 | $5,197 | |
| 2-10 | $8,437,285 | |
| 2-11 | $3,975,202 | |
| 2-14 | $1,323,996 | |
| 2-15 | $4,561,602 | |
| 2-16 | $309,288 | |
| 2-17 | $143,030 | |
| 2-18 | $484,358 | |
| 2-21 | $17,229,487 | |
| 2-22 | $3,986,141 | |
| Greece | 2-1 | $2,012 |
| 2-2 | $106,428 | |
| 2-9 | $9,908 | |
| 2-15 | $3,858 | |
| 2-21 | $9,908 | |
| 2-22 | $9,908 | |
| Greenland | 2-1 | $39,878 |
| Guatemala | 2-1 | $6,000 |
| Guyana | 2-3 | $58,000 |
| Hong Kong | 2-1 | $4,352 |
| 2-10 | $48,017,188 | |
| 2-15 | $20,000 | |
| Hungary | 2-7 | $4,992 |
| 2-21 | $115 | |
| India | 2-1 | $150,200 |
| 2-9 | $597,036 | |
| 2-10 | $4,186 | |
| 2-11 | $82,476 | |
| 2-13 | $46,200 | |
| 2-14 | $1,503,799 | |
| 2-15 | $36,000 | |
| 2-18 | $3,125 | |
| 2-21 | $1,503,799 | |
| 2-22 | $1,504,055 | |
| Indonesia | 2-1 | $41,900 |
| 2-5 | $11,070 | |
| 2-10 | $24,400 | |
| 2-15 | $625,000 | |
| 2-22 | $40,000 | |
| Iraq | 2-1 | $1,923,739 |
| 2-3 | $1,980 | |
| 2-22 | $50 | |
| Ireland | 2-1 | $2,987 |
| 2-6 | $66,400 | |
| 2-11 | $4,102 | |
| 2-13 | $15,317 | |
| 2-15 | $410,366 | |
| 2-22 | $29,620 | |
| Israel | 2-1 | $96,457 |
| 2-4 | $2,455,824 | |
| 2-5 | $748,561 | |
| 2-6 | $149,268 | |
| 2-9 | $1,002,838 | |
| 2-10 | $871,346 | |
| 2-11 | $2,273,472 | |
| 2-14 | $24,455 | |
| 2-15 | $71,572 | |
| 2-16 | $124,771 | |
| 2-18 | $10,846 | |
| 2-21 | $25,393 | |
| 2-22 | $19,826 | |
| Italy | 2-1 | $3,929,785 |
| 2-3 | $78,000 | |
| 2-5 | $125,130 | |
| 2-7 | $7,209 | |
| 2-9 | $16,000 | |
| 2-10 | $8,653,114 | |
| 2-11 | $876,136 | |
| 2-15 | $1,077,448 | |
| 2-16 | $368,754 | |
| 2-18 | $10,804 | |
| 2-21 | $32,298 | |
| 2-22 | $162,959 | |
| Japan | 2-1 | $4,088 |
| 2-2 | $6,629 | |
| 2-4 | $126,000 | |
| 2-9 | $82,014 | |
| 2-10 | $9,304,252 | |
| 2-11 | $605,208 | |
| 2-14 | $125,717 | |
| 2-15 | $120,274 | |
| 2-16 | $1,300,686 | |
| 2-21 | $1,896,276 | |
| 2-22 | $233,908 | |
| Jordan | 2-1 | $1,000 |
| 2-6 | $4,515,000 | |
| 2-11 | $208,845 | |
| 2-15 | $429,427 | |
| 2-18 | $77,381 | |
| 2-21 | $50,490 | |
| 2-22 | $68,481 | |
| Kazakhstan | 2-1 | $116,304 |
| 2-3 | $11,680 | |
| Kenya | 2-1 | $208,381 |
| 2-6 | $570,000 | |
| 2-15 | $2,061,212 | |
| Latvia | 2-1 | $2,114 |
| Lebanon | 2-1 | $762 |
| Liechtenstein | 2-1 | $636 |
| Lithuania | 2-15 | $12,753 |
| Luxembourg | 2-1 | $75,767 |
| 2-5 | $7,291 | |
| 2-6 | $7,291 | |
| 2-9 | $1,368,989 | |
| 2-10 | $483,053 | |
| 2-11 | $284,979 | |
| 2-15 | $9,774,034 | |
| 2-18 | $27,268 | |
| 2-22 | $73 | |
| Madagascar | 2-1 | $799 |
| Malaysia | 2-7 | $72,034 |
| 2-10 | $48,497 | |
| 2-18 | $765,546 | |
| Malta | 2-1 | $222 |
| Mexico | 2-11 | $4,485 |
| 2-14 | $40,000 | |
| 2-15 | $2,045,424 | |
| 2-18 | $9,000 | |
| 2-22 | $25,566 | |
| Montenegro | 2-1 | $153,932 |
| Morocco | 2-11 | $6,304 |
| 2-14 | $40,000 | |
| 2-21 | $250 | |
| 2-22 | $54 | |
| Namibia | 2-1 | $930 |
| Netherlands | 2-1 | $2,094,180 |
| 2-3 | $5,440 | |
| 2-4 | $1,195,200 | |
| 2-5 | $2,500 | |
| 2-6 | $47,264 | |
| 2-9 | $4,578,096 | |
| 2-10 | $3,137,905 | |
| 2-11 | $2,815,175 | |
| 2-14 | $6,935 | |
| 2-15 | $7,273,446 | |
| 2-16 | $70,856 | |
| 2-18 | $289,976 | |
| 2-21 | $270,007 | |
| 2-22 | $774,415 | |
| New Zealand | 2-1 | $90,619 |
| 2-2 | $1,075 | |
| 2-3 | $633,350 | |
| 2-5 | $1,734,415 | |
| 2-6 | $347,494 | |
| 2-10 | $2,954,088 | |
| 2-11 | $26 | |
| 2-14 | $54,632 | |
| 2-15 | $257,290 | |
| 2-21 | $100 | |
| 2-22 | $715 | |
| Nigeria | 2-6 | $1,260,000 |
| 2-10 | $436,671 | |
| 2-13 | $6,125 | |
| Norway | 2-1 | $166,522 |
| 2-2 | $223,612 | |
| 2-3 | $1,055,500 | |
| 2-5 | $145,841 | |
| 2-6 | $3,480,858 | |
| 2-7 | $4,935 | |
| 2-9 | $322,492 | |
| 2-10 | $15,000 | |
| 2-11 | $110,080 | |
| 2-15 | $2,434,497 | |
| 2-18 | $3,563 | |
| 2-21 | $28,279 | |
| 2-22 | $16,280 | |
| Oman | 2-1 | $357,174 |
| 2-4 | $1,655,598 | |
| 2-7 | $27,540 | |
| 2-11 | $2,192 | |
| 2-14 | $183,429 | |
| 2-21 | $278,166 | |
| 2-22 | $50,685 | |
| Peru | 2-1 | $140,140 |
| 2-6 | $19,444,625 | |
| 2-13 | $66,475 | |
| 2-22 | $500 | |
| Philippines | 2-10 | $192,490 |
| Poland | 2-1 | $316,992 |
| 2-2 | $17,400 | |
| 2-3 | $139,920 | |
| 2-7 | $66,545 | |
| 2-9 | $201,386 | |
| 2-10 | $103,638 | |
| 2-11 | $35,079 | |
| 2-18 | $1,234,640 | |
| 2-21 | $180 | |
| 2-22 | $760 | |
| Portugal | 2-9 | $557,148 |
| 2-10 | $53,657 | |
| 2-15 | $10,104 | |
| 2-22 | $40,000 | |
| Puerto Rico | 2-11 | $26,398 |
| 2-15 | $8,757 | |
| Qatar | 2-6 | $660,000 |
| Romania | 2-11 | $1,990 |
| Russian Federation | 2-1 | $1,599 |
| Saudi Arabia | 2-1 | $1,860,499 |
| 2-2 | $2,957,810 | |
| 2-3 | $6,092,760 | |
| 2-5 | $1,476,836 | |
| 2-6 | $71,259,172 | |
| 2-8 | $303,660 | |
| 2-11 | $37,598 | |
| 2-13 | $1,030,201 | |
| 2-14 | $1,023,891 | |
| 2-15 | $4,664,000 | |
| 2-18 | $189 | |
| 2-21 | $2,361,858 | |
| 2-22 | $2,572,230 | |
| Singapore | 2-1 | $11,000 |
| 2-3 | $6,373,173 | |
| 2-6 | $1,800,401 | |
| 2-7 | $132,240 | |
| 2-8 | $1,108,365 | |
| 2-10 | $2,069,953 | |
| 2-11 | $143,037 | |
| 2-14 | $42,727 | |
| 2-21 | $5,041 | |
| 2-22 | $45,499 | |
| Slovakia | 2-1 | $26,271 |
| Slovenia | 2-1 | $2,064 |
| 2-13 | $20,160 | |
| South Africa | 2-1 | $56,863 |
| 2-6 | $1,256,092 | |
| 2-11 | $1,552,787 | |
| 2-15 | $27,000 | |
| 2-17 | $1,177,350 | |
| 2-21 | $14,431 | |
| 2-22 | $250 | |
| South Korea | 2-1 | $30,464 |
| 2-5 | $99,418 | |
| 2-7 | $34,980 | |
| 2-9 | $5,337,066 | |
| 2-10 | $2,558,178 | |
| 2-11 | $2,685,452 | |
| 2-14 | $1,194,457 | |
| 2-15 | $31,001 | |
| 2-17 | $617,561 | |
| 2-18 | $294,375 | |
| 2-21 | $11,690 | |
| 2-22 | $1,516,001 | |
| Spain | 2-1 | $2,069 |
| 2-3 | $4,292,727 | |
| 2-6 | $101,680 | |
| 2-10 | $2,579,766 | |
| 2-11 | $692,636 | |
| 2-14 | $882,999 | |
| 2-15 | $1,305,888 | |
| 2-16 | $29,298 | |
| 2-17 | $164,720 | |
| 2-18 | $94,796 | |
| 2-21 | $5,607,664 | |
| 2-22 | $4,124,864 | |
| St. Kitts-Nevis | 2-3 | $450 |
| Sweden | 2-1 | $37,083 |
| 2-3 | $17,712 | |
| 2-4 | $14,000 | |
| 2-5 | $1,198 | |
| 2-6 | $8,309,791 | |
| 2-9 | $386,181 | |
| 2-10 | $1,292,858 | |
| 2-11 | $134,589 | |
| 2-14 | $130,987 | |
| 2-15 | $13,640 | |
| 2-17 | $1,226,940 | |
| 2-21 | $607,417 | |
| 2-22 | $879,888 | |
| Switzerland | 2-1 | $144,197 |
| 2-3 | $385,520 | |
| 2-5 | $1,440,849 | |
| 2-6 | $1,500,418 | |
| 2-7 | $299,700 | |
| 2-10 | $976,231 | |
| 2-11 | $181,581 | |
| 2-15 | $1,785,604 | |
| 2-21 | $389,189 | |
| 2-22 | $41,235 | |
| Taiwan | 2-11 | $307,892 |
| 2-17 | $73 | |
| 2-21 | $80,000 | |
| 2-22 | $41,450 | |
| Tanzania | 2-1 | $300 |
| 2-3 | $160 | |
| Thailand | 2-1 | $8,141 |
| 2-10 | $6,032,403 | |
| 2-11 | $10,728 | |
| 2-13 | $3,625 | |
| 2-22 | $40,000 | |
| Tunisia | 2-10 | $5,989,166 |
| Turkey | 2-1 | $1,600 |
| 2-5 | $544,876 | |
| 2-6 | $171,164 | |
| 2-10 | $369,537 | |
| 2-14 | $323,832 | |
| 2-15 | $4,034,089 | |
| 2-17 | $122,357 | |
| 2-21 | $1,847,410 | |
| 2-22 | $142,689 | |
| Ukraine | 2-1 | $109,871 |
| 2-11 | $44,994 | |
| 2-22 | $270 | |
| United Arab Emirates | 2-1 | $1,423,938 |
| 2-6 | $351,051 | |
| 2-10 | $1,004,295 | |
| 2-11 | $19,495 | |
| 2-15 | $119,500 | |
| 2-17 | $589,020 | |
| 2-18 | $24,400 | |
| 2-21 | $3,750 | |
| 2-22 | $94,279 | |
| United Kingdom | 2-1 | $4,153,821 |
| 2-2 | $45,120 | |
| 2-3 | $3,526,337 | |
| 2-4 | $945,117 | |
| 2-5 | $6,113,465 | |
| 2-6 | $699,871 | |
| 2-9 | $19,862,804 | |
| 2-10 | $9,262,885 | |
| 2-11 | $13,690,394 | |
| 2-13 | $1,935 | |
| 2-14 | $11,632,716 | |
| 2-15 | $12,510,263 | |
| 2-16 | $976,593 | |
| 2-17 | $250,133 | |
| 2-18 | $982,570 | |
| 2-21 | $10,033,332 | |
| 2-22 | $7,173,190 | |
| Vietnam | 2-1 | $6,482 |
| Yemen | 2-15 | $32,000 |
| Member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization | Automatic Firearms Country Control List (AFCCL) | Participating States of the Wassenaar Arrangement |
|---|---|---|
| Albania Belgium Bulgaria Canada Croatia Czech Republic Denmark Estonia France Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Italy Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Netherlands Norway Poland Portugal Romania Slovakia Slovenia Spain Turkey United Kingdom United States | Albania Australia Belgium Botswana Bulgaria Chile Colombia Croatia Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Israel Italy Kuwait Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Netherlands New Zealand Norway Peru Poland Portugal Romania Saudi Arabia Slovakia Slovenia South Korea Spain Sweden Turkey United Kingdom United States | Argentina Australia Austria Belgium Bulgaria Canada Croatia Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Germany Greece Hungary Ireland Italy Japan Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Mexico Netherlands New Zealand Norway Poland Portugal Romania Russia Slovakia Slovenia South Africa South Korea Spain Sweden Switzerland Turkey Ukraine United Kingdom United States |
Footnotes
- Footnote *
If you require a plug-in or a third-party software to view this file, please visit the alternative formats section of our help page.
- Footnote 1
Note that due to long-standing bilateral agreements between Canada and the United States, most exports of military goods and technology move between our two countries permit free. Therefore, Canadian exports to the United States are not captured by the statistics contained in this Report.
- Footnote 2
More information about Canada’s export controls, including the publication A Guide to Canada’s Export Controls, which contains the Export Control List, can be found on the Internet.
- Footnote 3
More information about economic sanctions imposed by Canada, including arms embargoes against a number of countries, can be found on the Internet.
- Footnote 4
Subsection 84(1) of the Criminal Code provides definitions of “non-restricted firearm” and “restricted firearm”.
- Footnote 5
Subsection 84(1) of the Criminal Code provides definitions of “prohibited firearm”, “prohibited weapon” and “prohibited device”.
- Footnote 6
More information about Canada’s non-proliferation policies can be found on the Internet.
- Footnote 7
More information about the Wassenaar Arrangement can be found on the Internet.
- Footnote 8
More information about the United Nations Register of Conventional Arms can be found on the Internet.
- Footnote 9
Exports to the United States are not included in this report. Please see data interpretation notes.
- Footnote 10
Categories are based on the 2015 Human Development Index as presented in the UN Development Programme Human Development Report 2015.
- Footnote 11
A list of member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is presented in Table 8.
- Footnote 12
A list of countries on the Automatic Firearms Country Control List (AFCCL) is presented in Table 8.
- Footnote 13
Data for this table is taken from the “Annual Report to Parliament on the Administration of the Export and Import Permits Act.” The information for this table is drawn from the Export Controls Online (EXCOL), an online database used to process export permit applications. The information on EXCOL is not publically available. Unlike the information presented throughout the report, which only covers Group 2 items, this table covers all control groups; Group 2 is highlighted.
- Footnote 14
Exports to the United States are not included in this report. Please see data interpretation notes.
- Footnote 15
Exports to the United States are not included in this report. Please see data interpretation notes.
- Footnote 16
Exports to the United States are not included in this report. Please see data interpretation notes. Table 3 is a listing of Canada’s top destinations outside of the United States military items by value. Canada’s “Annual Report to Parliament on the Administration of the Export and Import Permits Act” contains a chart that reflects the top 12 destinations by number of permits issued for all military, dual-use and strategic items on the Export Control List.
- Footnote 17
Table does not include the United States. Please refer to Data Interpretation Notes.
- Footnote 18
The full list of goods and technology, including precise definitions of the terms used in the table, may be found in A Guide to Canada’s Export Controls, available on the Internet.
- Footnote 19
Exports to the United States are not included in this report. Please see data interpretation notes.
- Footnote 20
Exports to the United States are not included in this report. Please see data interpretation notes.
- Date modified: